You may use Microsoft Windows Storage Server 2012 as an iSCSI Storage Area Network (SAN). To do so you must install the iSCSI Target feature. Below you will find a step-by-step guide to installing this feature.
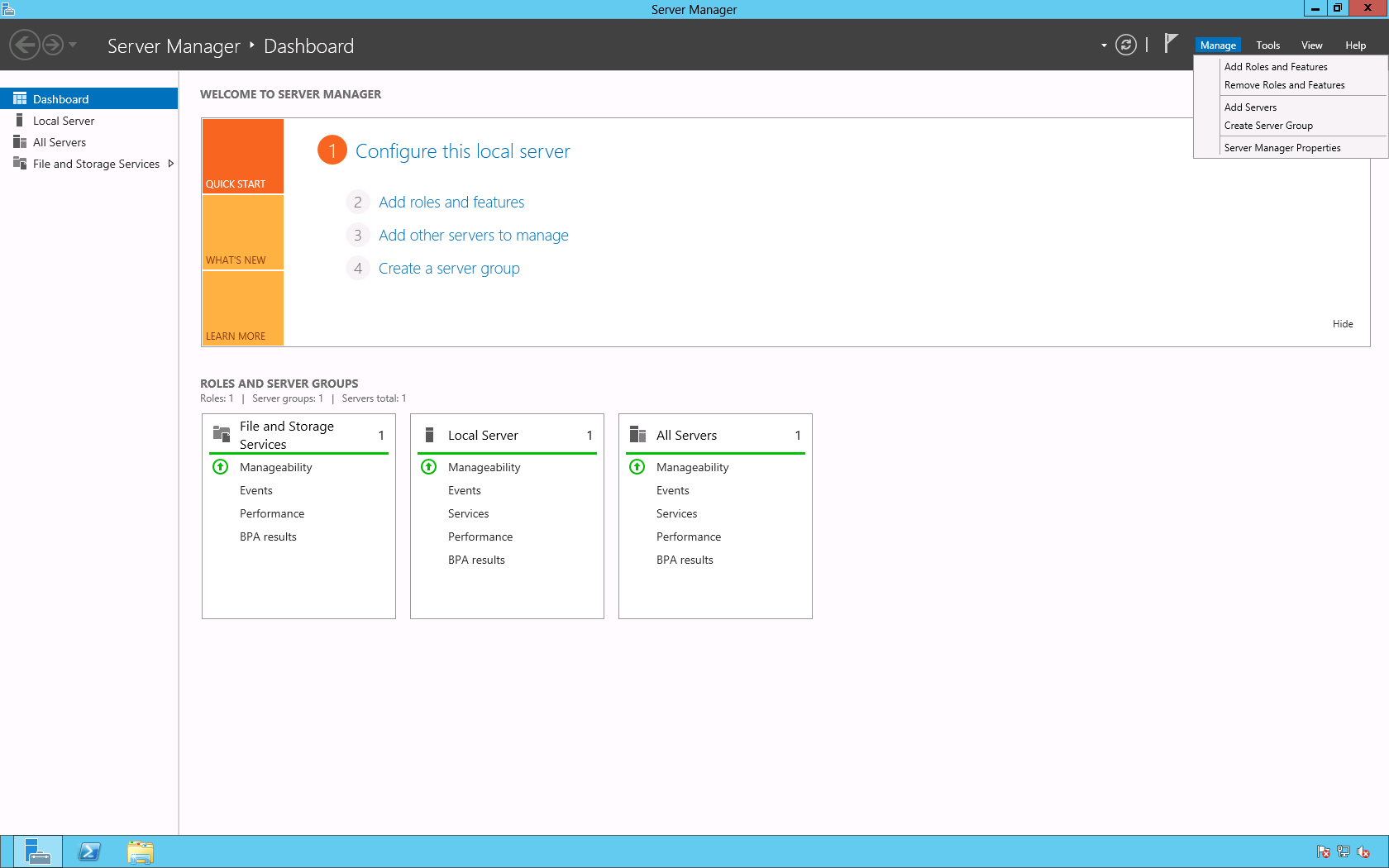
On the Server Manager > Dashboard page select Manage > Add Roles and Features.
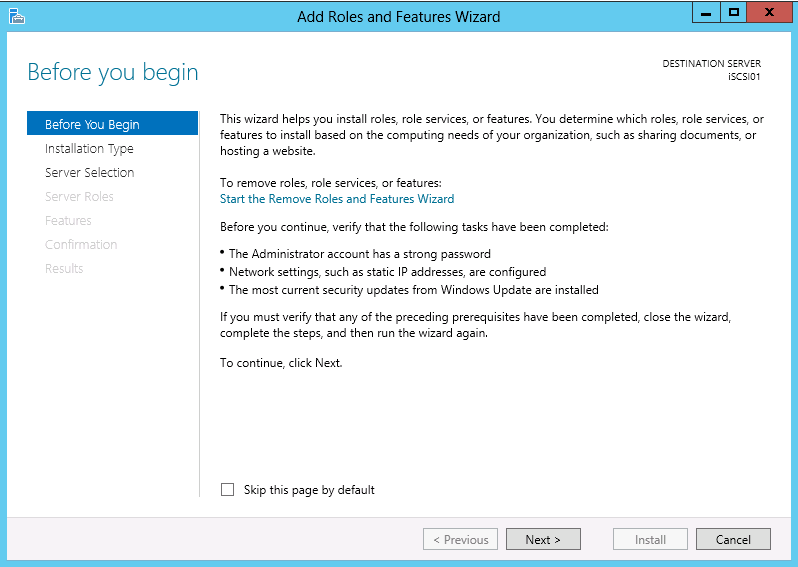
On the Before you begin page click Next >.
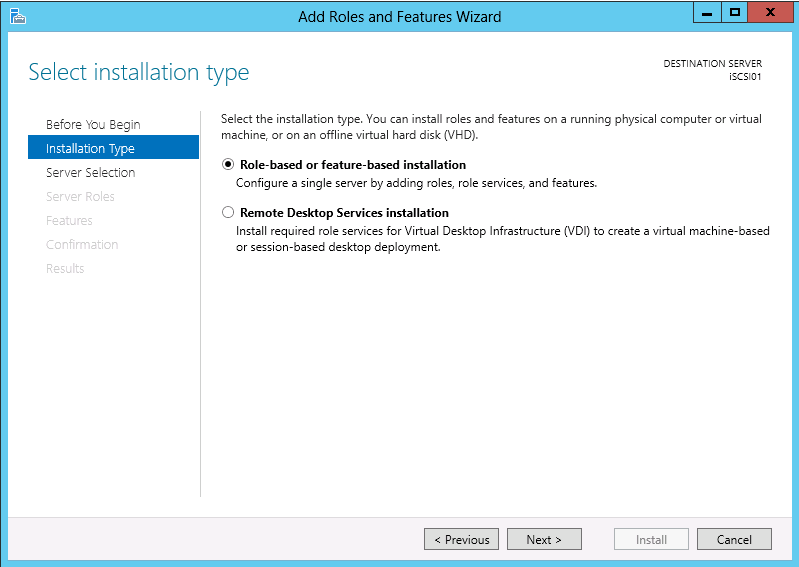
On the Installation Type page select Role-based or feature-based installation and click Next >.
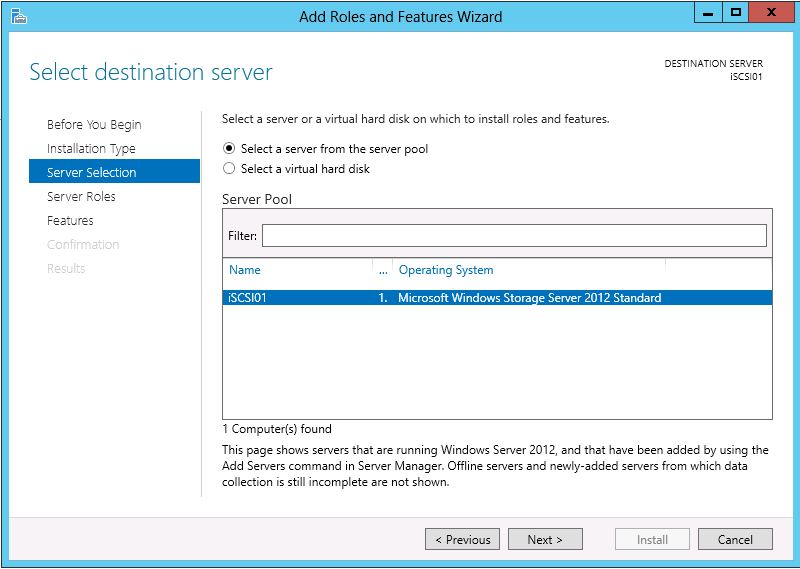
On the Server Selection page select the server that you would like to enable the iSCSI Target. In this example, I will be choosing iSCSI01. After selecting the server click Next >.
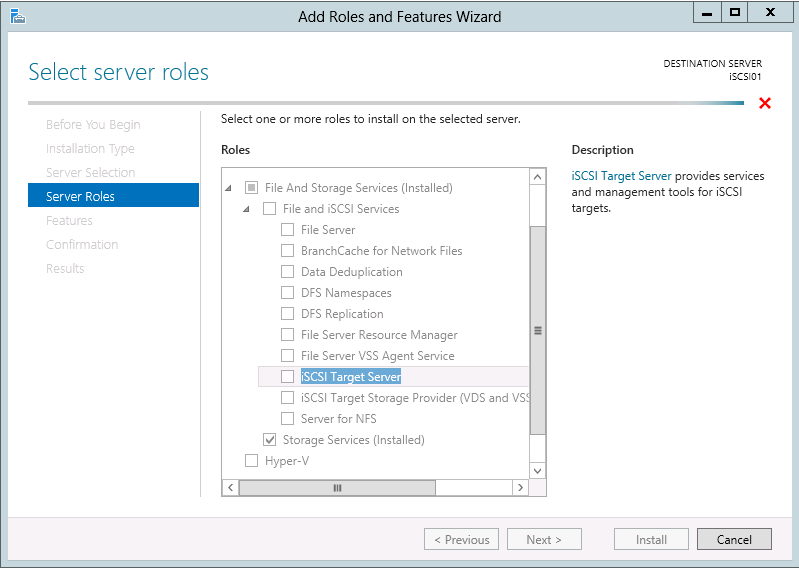
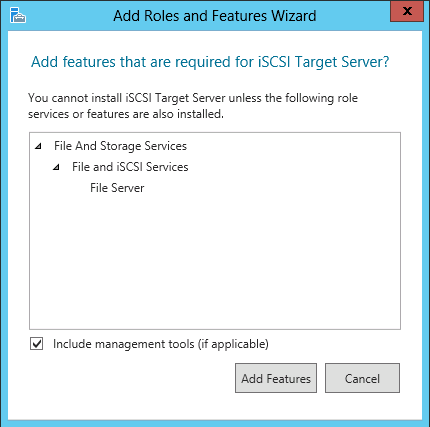
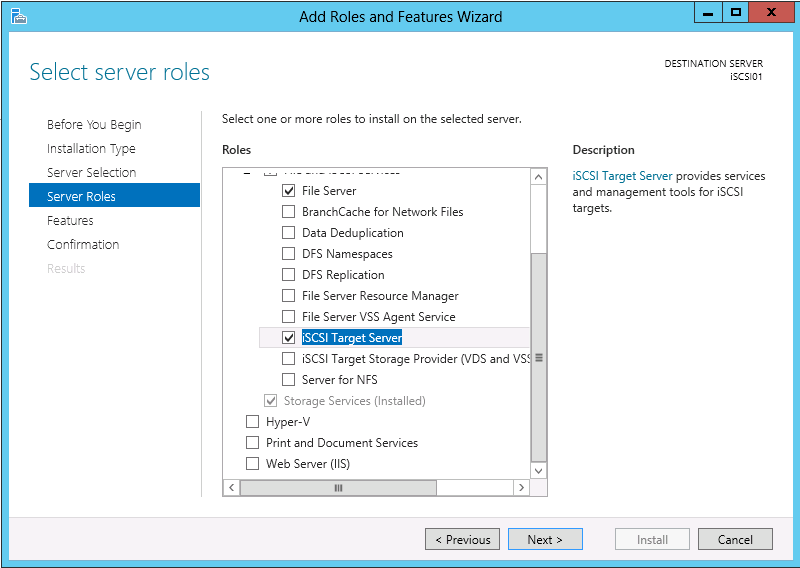
On the Server Roles page select File And Storage Services (Installed) > File and iSCSI Services > iSCSI Target Server. When the Add features that are required for iSCSI Targer Server? dialog box appears click Add Features. When you return to the Server Roles page click Next >.
On the Features page click Next >.
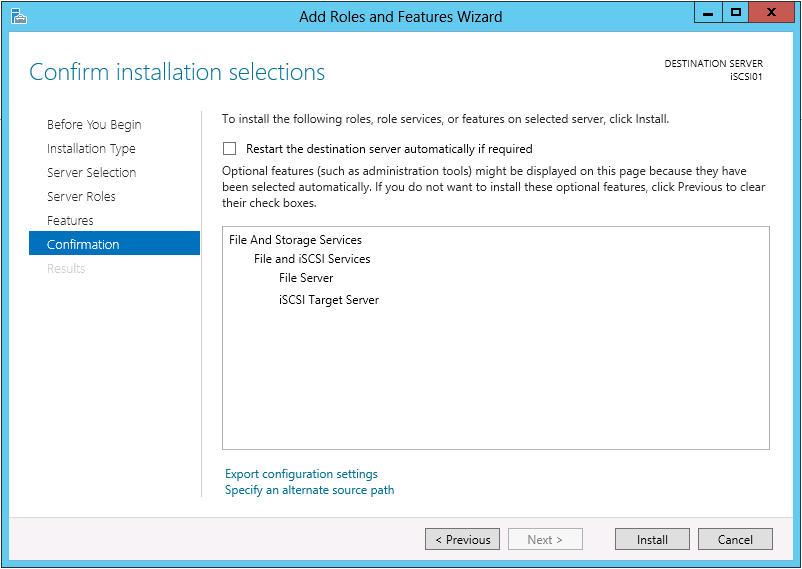
On the Confirmation page click Install.
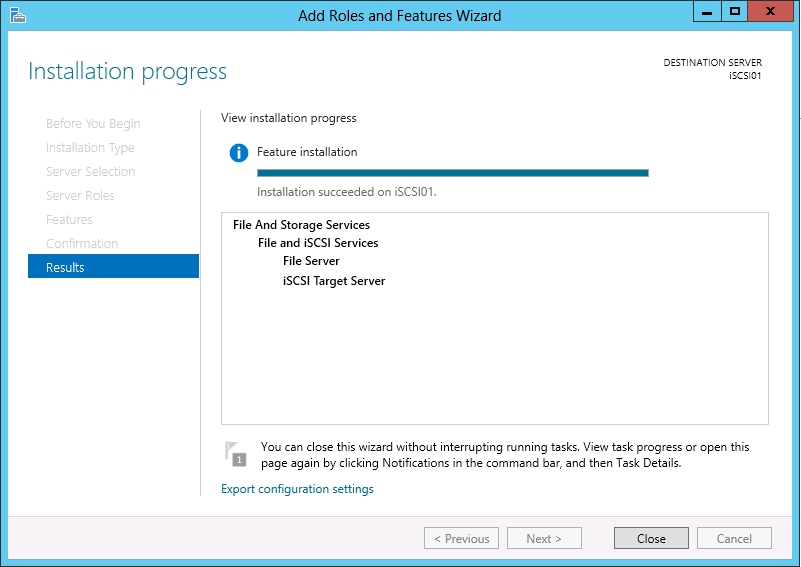
On the Results page verify that the installation was successful (i.e. Installation succeeded on server), then click Close.
This completes the installation.
Enjoy!