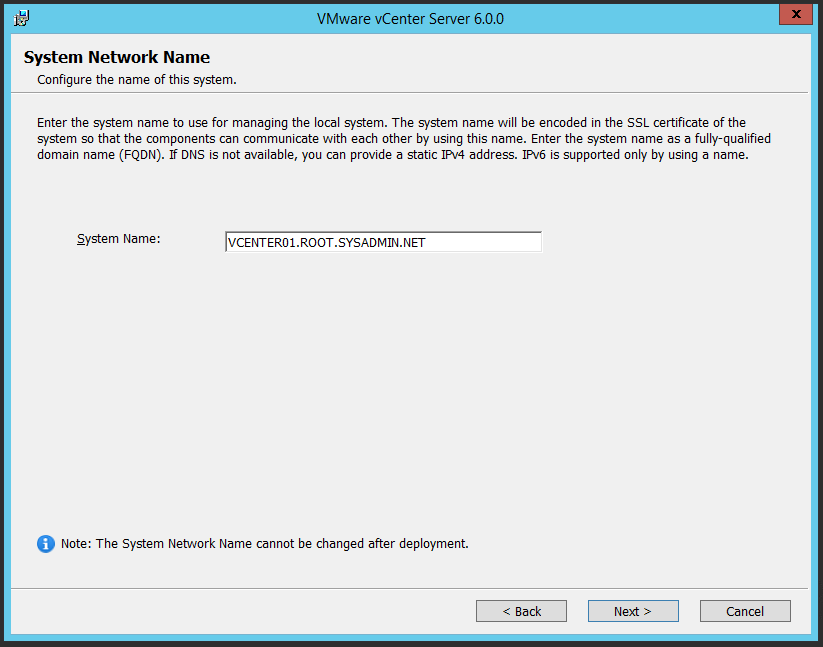
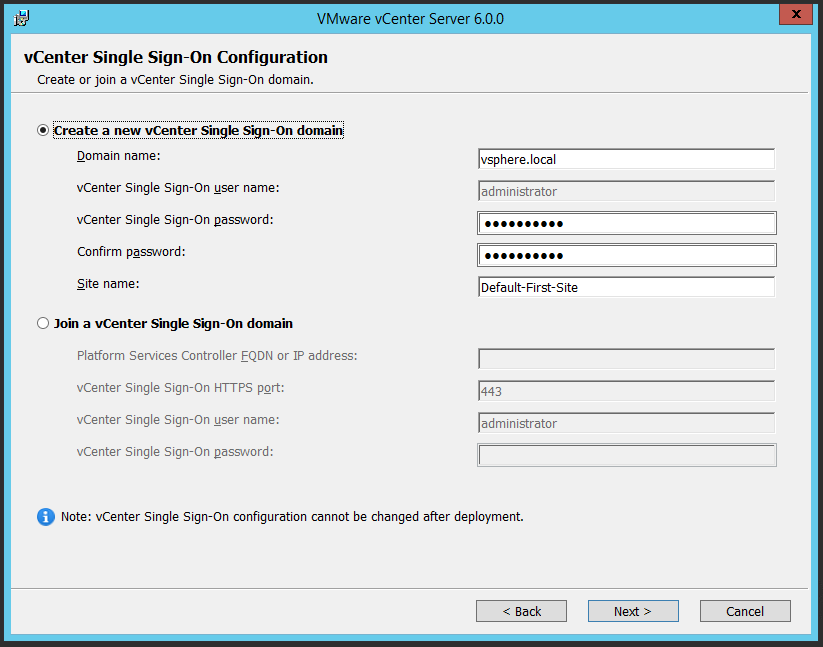
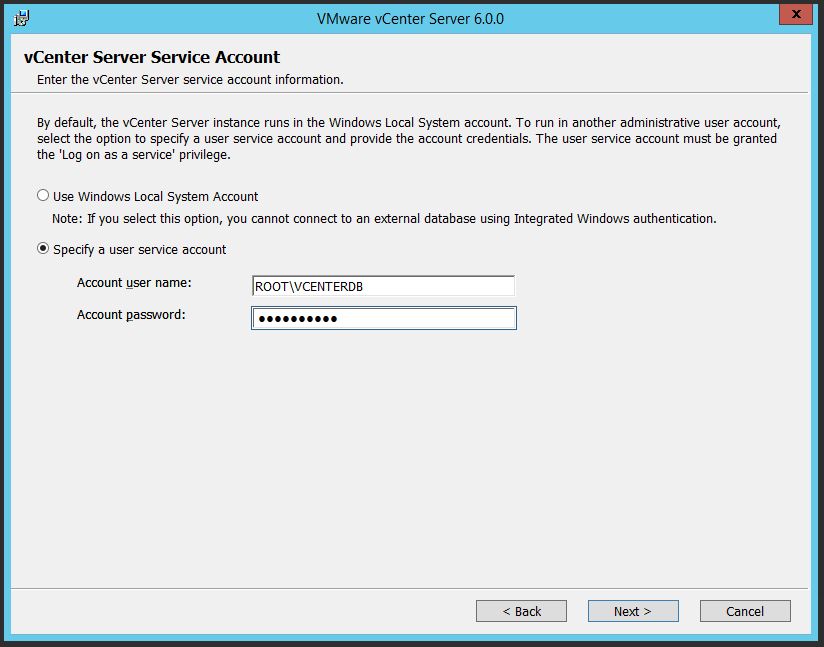
You may use the following Microsoft Windows PowerShell script to export the users in a Microsoft Active Directory group to a notepad (.txt) file. Additionally, please edit the out-file -filepath portion of this script to a network location of your choice.
<#
.SYNOPSIS
This script will provide the members of a Microsoft Active Directory group and export them to a notepad (.txt) file.
.DESCRIPTION
This script automates the process of exporting the users in a Microsoft Active Directory group.
.EXAMPLE
N/A.
.AUTHOR
Written by Noel Enrique Alvarez on Thursday, March 17, 2016.
#>
#Import the Microsoft Active Directory module
Import-Module ActiveDirectory
#Request the name of the Microsoft Active Directory group
$GROUP = Read-Host “What is the name of the Microsoft Active Directory group?”
#Export the members of the Microsoft Active Directory group and export them.
Get-ADGroupMember -identity $GROUP | Select Name, SamAccountName | out-file -filepath “C:\Users\User01\Desktop\$GROUP.txt”